Orthopaedics covers several diseases that impair everyday life and movement. Maintaining long-term musculoskeletal health requires understanding these disorders and their treatments, from joint discomfort and fractures to back and tendon problems. We’ll discuss common orthopaedic problems, their causes, symptoms, and pain-relieving treatments in this post.
1. Osteoarthritis and Joint Pain Management
Osteoarthritis (OA) is one of the most common and disabling orthopedic conditions, often affecting joints like the knees, hips, and hands. It occurs when the cartilage that cushions the joints wears down, leading to pain, stiffness, and inflammation. Early-stage OA is managed through conservative treatments such as physical therapy, exercise, and anti-inflammatory medications.
| Treatment Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | Strengthens muscles around the joint, improving mobility. |
| Exercise | Low-impact activities like swimming or cycling. |
| Medications | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). |
| Joint Replacement | In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be necessary. |
For advanced OA, corticosteroid injections or even joint replacement surgery may be considered.
2. Tendinitis and Overuse Injuries
Tendinitis is the inflammation or irritation of a tendon, typically caused by repetitive movement or overuse. Common sites include the shoulder, elbow, wrist, and knee. Initial treatment involves rest, ice, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and swelling.
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Rest | Reduces stress on the affected tendon. |
| Ice | Helps reduce swelling and pain. |
| Physical Therapy | Restores function and flexibility. |
| Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) | Advanced treatment option for chronic tendinitis. |
In chronic cases, treatments like PRP injections or surgical intervention may be considered to promote healing.
3. Fractures and Bone Healing
Fractures occur when bones break due to trauma, such as falls or accidents. Proper medical attention is critical to ensure correct bone healing and prevent long-term issues. Diagnosis typically involves imaging techniques like X-rays or CT scans. Treatment may involve immobilization with a cast or surgery in severe cases.
| Treatment Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Cast/Splint | Immobilizes the broken bone to allow healing. |
| Surgery (Internal Fixation) | Uses metal plates, screws, or rods to align bones. |
| Rehabilitation | Physical therapy to restore mobility and strength. |
Proper follow-up care is essential for monitoring recovery and preventing complications.

4. Lower Back Pain and Spinal Conditions
Lower back pain is a widespread issue, often caused by poor posture, muscle strain, or degenerative disc disease. It can lead to significant discomfort and disability. Non-surgical interventions include physical therapy, posture corrections, and chiropractic care.
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | Strengthens back muscles and improves posture. |
| Chiropractic Care | Helps realign the spine and relieve pressure. |
| Spinal Injections | Used to reduce inflammation and manage pain. |
When conservative treatments fail, surgery may be required to alleviate nerve compression or disc problems.
5. Understanding Bone Health and Nutrition
Bone health plays a crucial role in preventing fractures and managing conditions like osteoarthritis. Ensuring adequate intake of calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients is vital for maintaining bone strength.
| Nutrient | Function |
|---|---|
| Calcium | Strengthens bones and teeth. |
| Vitamin D | Aids calcium absorption. |
| Magnesium | Important for bone formation and strength. |
Including these nutrients in your diet or taking supplements when needed can help support bone health throughout life.
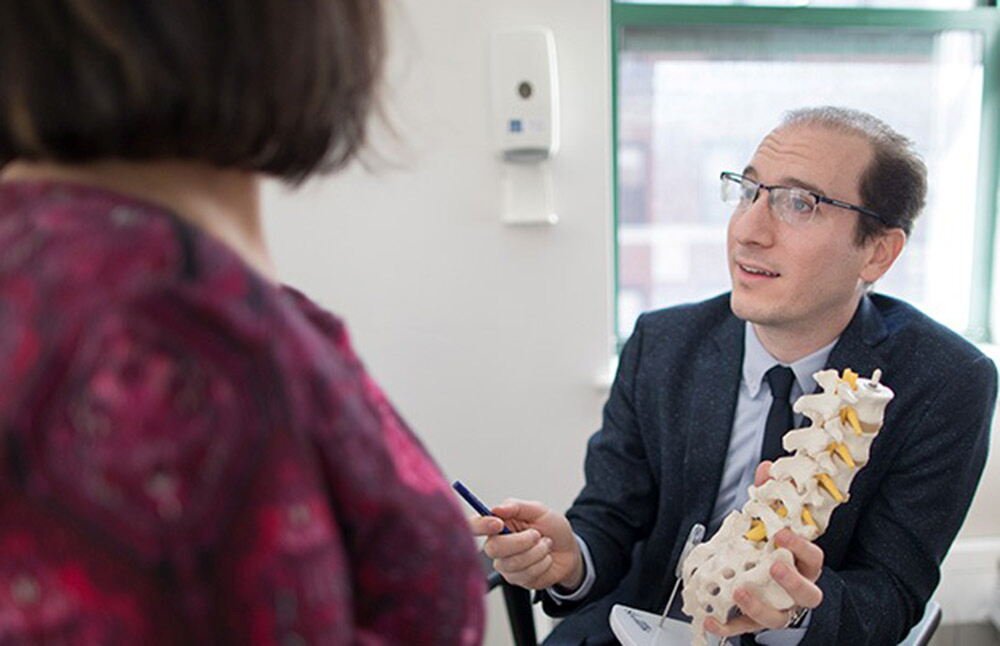

6. Surgical Interventions in Orthopedics
Some orthopaedic disorders require surgery, but most may be treated non-surgically. Joint replacement, spinal surgery, and fracture repair relieve pain and restore function. Surgery typically uses minimally invasive methods to lessen recovery time and risks.

7. Physical Therapy: The Backbone of Recovery
Physical therapy plays a critical role in the rehabilitation of various orthopedic conditions. Whether recovering from surgery, managing a fracture, or treating chronic pain, physical therapy focuses on improving mobility, strength, and function through exercises and hands-on techniques.

8. Managing Chronic Pain in Orthopedics
Quality of life can be greatly affected by chronic orthopaedic discomfort. Medication, physical therapy, acupuncture, and massage are used to manage pain. Multidisciplinary management of chronic orthopaedic diseases frequently yields the greatest outcomes.

9. Post-Surgical Rehabilitation
After orthopedic surgeries such as joint replacements or spine surgery, rehabilitation is essential for restoring mobility and strength. Post-surgical rehabilitation often involves a personalized exercise program, pain management techniques, and close monitoring of recovery progress.
10. Preventing Overuse Injuries
Tendinitis and stress fractures frequently arise from repeated muscle and tendon tension. Prevention methods include warm-ups, stretching, ergonomic gear, and good body mechanics during exercise.
11. The Role of Ergonomics in Orthopedic Health
Ergonomics involves designing work and living spaces that reduce strain on the body. Proper ergonomics can help prevent musculoskeletal disorders, especially for people who spend long hours sitting or engaging in repetitive tasks.
12. Innovative Treatments in Orthopedics
In recent years, innovative treatments like stem cell therapy and PRP injections have gained popularity for their ability to promote healing and tissue regeneration. These treatments are particularly beneficial for conditions like tendinitis, arthritis, and ligament injuries.
13. The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of orthopedic conditions is crucial for successful treatment. Delaying medical attention can lead to more severe damage and longer recovery times. Regular check-ups and consultations with an orthopedic specialist can help identify potential issues before they become debilitating.
14. Conclusion: Maintaining Musculoskeletal Health
Orthopedic health is essential for maintaining an active and fulfilling life. By understanding common conditions and their treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps toward managing their musculoskeletal health. Whether through lifestyle changes, physical therapy, or advanced surgical interventions, it’s important to seek professional care to restore function and reduce pain.
For personalized treatment plans and further guidance, always consult an orthopedic specialist to address your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is the breakdown of joint cartilage, leading to pain and stiffness. It mostly affects the knees, hips, and hands.
How can tendinitis be treated?
Tendinitis is treated with rest, ice, medication, and physical therapy. Severe cases may require injections or surgery.
What are common causes of lower back pain?
Poor posture, muscle strain, and herniated discs are common causes of lower back pain.
When should I consider surgery for orthopedic conditions?
Surgery is typically considered when non-surgical treatments don’t provide relief, or if there’s significant nerve compression.
How can I prevent orthopedic injuries?
Proper warm-up, stretching, using ergonomic tools, and maintaining good posture can prevent many injuries.











