Sanitation and cleanliness are crucial in the food industry’s growing worldwide market. These measures promote consumer safety and food industry success and longevity. Sanitation and cleanliness are essential for food safety, contamination prevention, and customer confidence. This article discusses food safety basics, industrial issues, and public health technologies and practises.
1. Food Safety: The Cornerstone of Public Health
Foodborne illnesses remain a significant global health threat, with millions of people affected each year. Ensuring food safety is vital in preventing outbreaks of diseases such as E. coli, salmonella, and listeria, which can severely impact vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and those with compromised immune systems.
Regulatory bodies, such as the FDA and WHO, have established strict guidelines for the food industry. These guidelines are designed to ensure that food is safe, nutritious, and free from contaminants. Proper food safety practices, including proper storage, handling, and preparation, significantly reduce the risk of contamination.
2. The Role of Sanitation and Hygiene
The simplest yet most effective method of ensuring food safety is maintaining high standards of sanitation and hygiene throughout the entire food supply chain. While the intricacies of food safety might seem complex, basic hygiene practices such as regular handwashing, equipment sanitization, and cleanliness of food production areas are the backbone of preventing contamination.
Ignoring hygiene can lead to the spread of pathogens that cause gastrointestinal diseases, which can result in public health crises. It’s essential for food establishments to enforce rigorous cleaning protocols and to train staff on proper hygiene practices.
3. Types of Food Hazards
Foodborne hazards are categorized into three primary types: physical, chemical, and biological. Each type presents its own unique challenges, but all pose risks that can compromise food safety.
| Hazard Type | Examples | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Physical | Metal, glass, plastic particles | Physical injury, contamination, and consumer harm |
| Chemical | Pesticides, heavy metals, harmful additives | Toxicity, poisoning, long-term health effects |
| Biological | Bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites | Foodborne illnesses, outbreaks, severe health risks |
Identifying and controlling these hazards is crucial in ensuring the food remains safe from production to consumption.
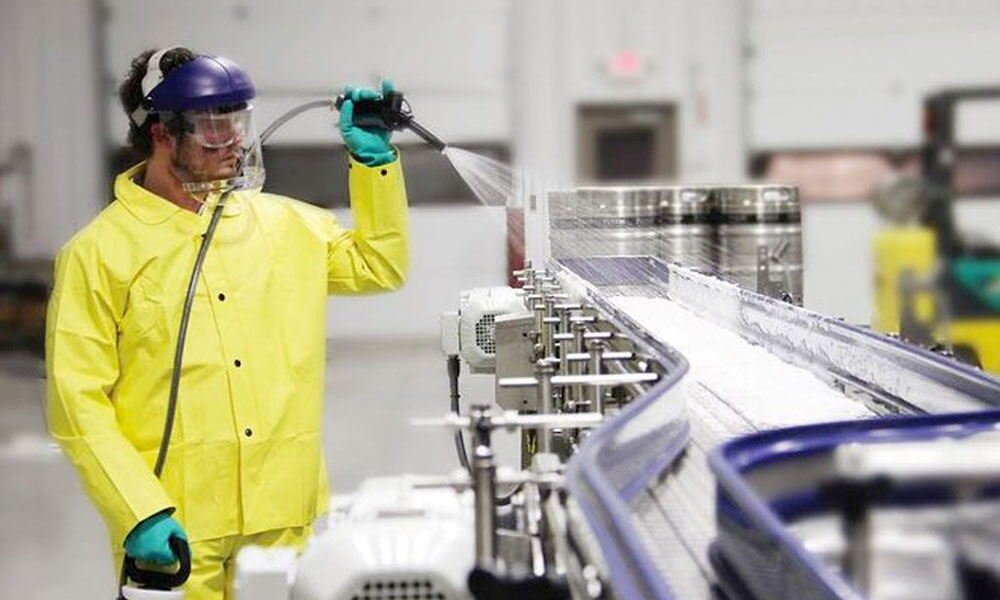

4. Preventing Physical Hazards
Physical hazards can occur when foreign objects such as glass, metal, or plastic inadvertently enter food during processing. These hazards are preventable through proper facility maintenance, rigorous inspection procedures, and the use of detection technologies.
A simple but effective measure is the use of metal detectors in food processing plants. These systems identify foreign metallic objects before they can reach the consumer, ensuring the integrity of the food product.
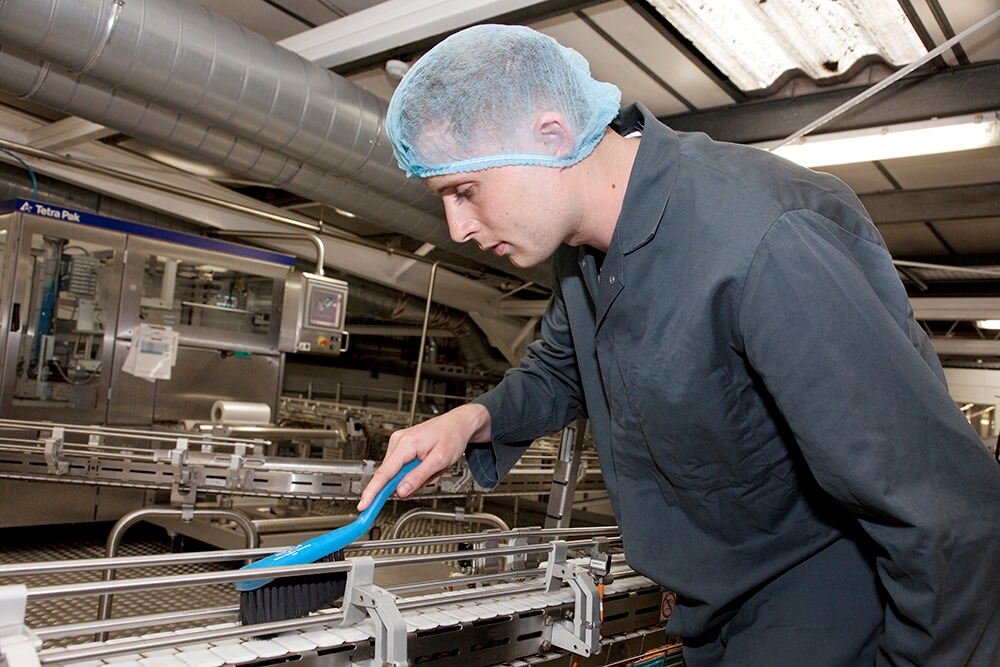

5. Addressing Chemical Hazards
Chemical hazards in food can result from improper use of pesticides, preservatives, or sanitizing agents. These chemicals, when consumed in excess or when they are present in unauthorized forms, can cause poisoning or long-term health issues.
The key to mitigating chemical risks lies in adhering to regulatory standards and using advanced detection technologies such as spectroscopy. Spectrometers can identify harmful chemical substances in food, ensuring they are within permissible limits and do not pose a risk to human health.
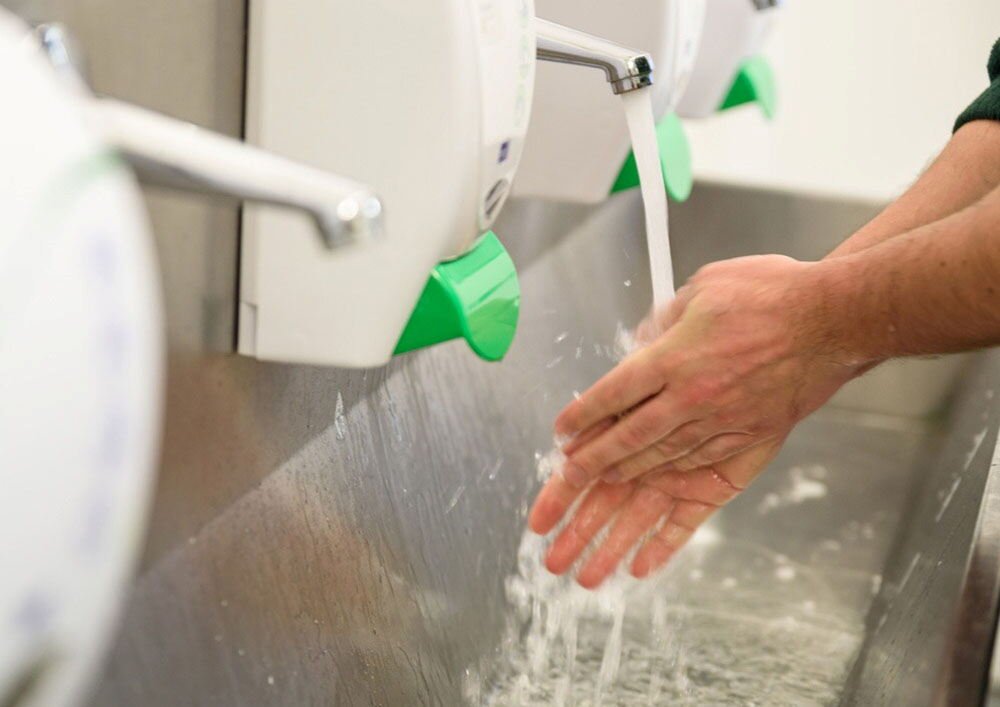

6. Combatting Biological Hazards
Bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites are biological hazards that can contaminate food, leading to foodborne illnesses. These pathogens often thrive in moist, warm environments, making proper temperature control and sanitation critical to preventing outbreaks.
Routine monitoring for pathogens through microbiological testing, combined with an effective sanitation program, helps mitigate the risk of biological contamination.

7. The Importance of Hygiene Standards
Hygiene practices are among the most effective ways to prevent contamination and maintain food safety. All food processing personnel must adhere to stringent hygiene protocols, including wearing appropriate protective gear, such as gloves, hairnets, and face masks.
Maintaining a clean work environment, especially in areas where food is handled, reduces the risk of cross-contamination and ensures that food products remain safe for consumers.

8. Color-Coding in Food Processing
Food processing facilities use colour-coding to avoid cross-contamination. These systems employ distinct colours for various jobs or locations to prevent interaction between food-type-specific equipment and utensils.
Raw meats may be red, dairy white, and veggies green. It reduces allergen contamination and avoids raw and ready-to-eat food cross-contact.

9. Technology and Its Impact on Food Safety
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the food industry’s approach to sanitation and safety. Tools such as cloud-based software solutions help businesses monitor and manage sanitation schedules in real-time. These technologies also provide centralized reporting and tracking, ensuring compliance with safety regulations across all facilities.
In addition, innovations in detection technologies, such as infrared spectroscopy and biosensors, allow for faster and more accurate identification of contaminants, helping to streamline the food safety process.

10. Cloud-Based Systems for Sanitation
Cloud technology has become a game-changer for food safety management. By using cloud-based software, businesses can create customized sanitation protocols, monitor cleaning schedules, and track compliance from any location.
These systems offer real-time data analytics, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and identify potential hazards before they escalate into bigger problems.

11. Reducing Food Waste Through Proper Sanitation
Proper sanitation not only protects public health but also reduces food waste. By minimizing contamination during the food production process, manufacturers can ensure that products meet safety standards, reducing the need to discard batches of food.
Additionally, reducing waste aligns with sustainability goals, ensuring that food is not wasted due to preventable safety issues.

12. Food Safety and Global Trade
Businesses seeking worldwide trading must follow international food safety requirements. Food manufacturers in the EU and US must fulfil exacting criteria to protect consumer safety.
These worldwide standards streamline international trade and guarantee products satisfy global customer expectations.

13. The Economic Impact of Food Safety
The global food industry is valued at over $9 trillion, and food safety plays a crucial role in the economic success of this sector. The adoption of stringent safety measures and the continuous improvement of sanitation protocols can significantly reduce the risk of costly recalls, lawsuits, and damage to brand reputation.
Investing in food safety is not just a regulatory obligation; it is also a sound business decision that can lead to long-term profitability and consumer loyalty.

14. Training and Education for Food Safety
Businesses must train and educate personnel to guarantee food safety rules are followed. Staff should be informed about new sanitation, food safety, and risk management techniques.
Training programs should emphasise hygiene and sanitation and provide workers the skills and knowledge to keep the workplace clean.
15. Looking to the Future of Food Safety
As the food industry continues to grow, innovations in sanitation and safety will continue to evolve. Emerging technologies, such as AI-driven monitoring systems and advanced pathogen detection methods, promise to further enhance food safety.
By staying ahead of these trends and committing to the highest standards of sanitation and hygiene, the food industry can continue to safeguard public health and ensure a sustainable, thriving global market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of food hazards?
There are three main types: physical, chemical, and biological. Each poses unique risks to food safety.
Why is hygiene important in the food industry?
Hygiene prevents contamination, ensuring the safety and quality of food products. It protects both consumers and businesses.
How does technology improve food safety?
Technology like cloud systems and spectroscopy helps monitor sanitation, detect hazards, and ensure compliance in real-time.
What are the consequences of poor sanitation?
Poor sanitation can lead to foodborne illnesses, recalls, loss of consumer trust, and financial losses.
How can food businesses prevent contamination?
Businesses can use color-coding, regular cleaning, proper training, and advanced detection technologies to prevent contamination.